
Scroll down to see all the illustrations on the page








Pages






T A N K


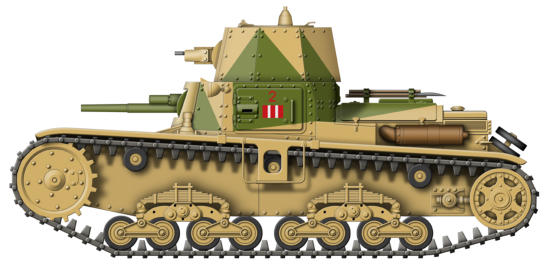
Carro Armato M11/39
The design of the M11/39 was influenced by the British Vickers
E tank, particularly in the track and suspension design. The
main armament was located in a sposon mounted in the hull
front, while a one man turret was armed with twin 8 mm
machine guns. Further development resulted in a model with
eight road wheels and this basic chassis was used for all
subsequent Italian medium tanks. Only 100 M 11/39s were
built as the design was already considered obsolete, medium
tank production then being concentrated on the M13/40 which
was a superior design. Seventy-two M11/39 tanks were sent to
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Weight: 11 tons
Dimensions: Length 15 ft 5 ins, Width 7 ft 2 ins, Height 7 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 105 hp SPA diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 20 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 37 mm gun, 2 x 8 mm Breda machine guns
Armour: Maximum thickness 30 mm
Crew: 3
North Africa after Italy entered World War Two on the side of
Germany. During the Italian advance into Egypt the type was
totally outclassed by the British A9 and A10 cruisers and a
small number of Matilda tanks, many being captured or
destroyed during the British counter-offensive. Twenty-four
were also sent to support Italian forces in East Africa where
they were also destroyed or captured. During the siege of
Tobruk captured M11s were used by the Australians (who
painted a large white kangaroo on the turrets) and used them
against their former owners until they ran out of diesel fuel.
Country of Origin: Italy
Number Built: 100
T A N K










Pages
































