
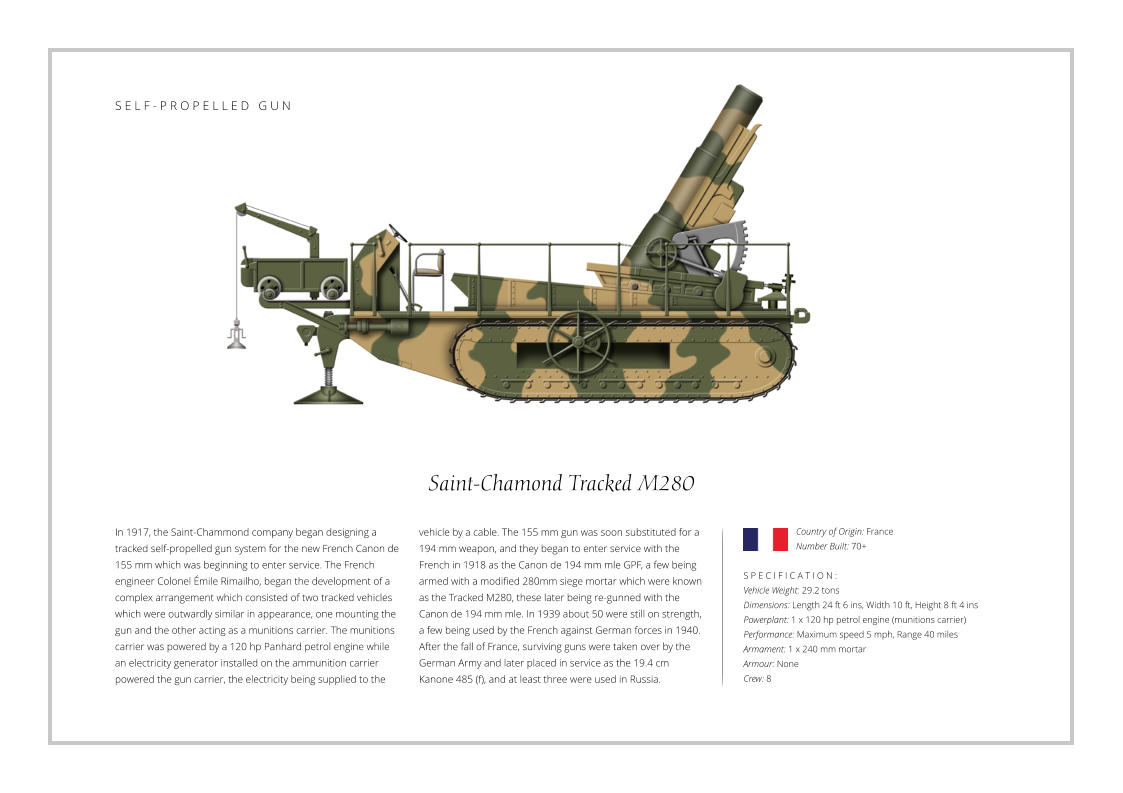
Scroll down to see all the illustrations on the page








Pages







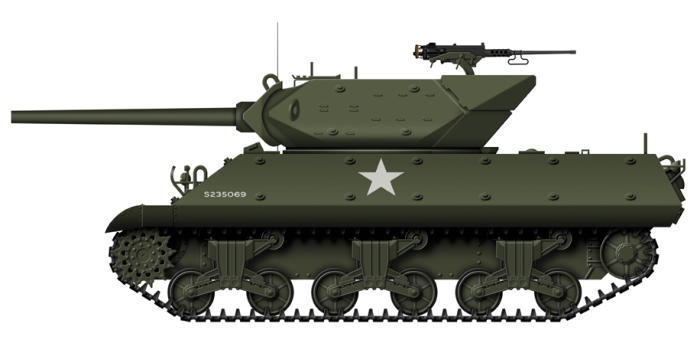
M10 Gun Motor Carriage
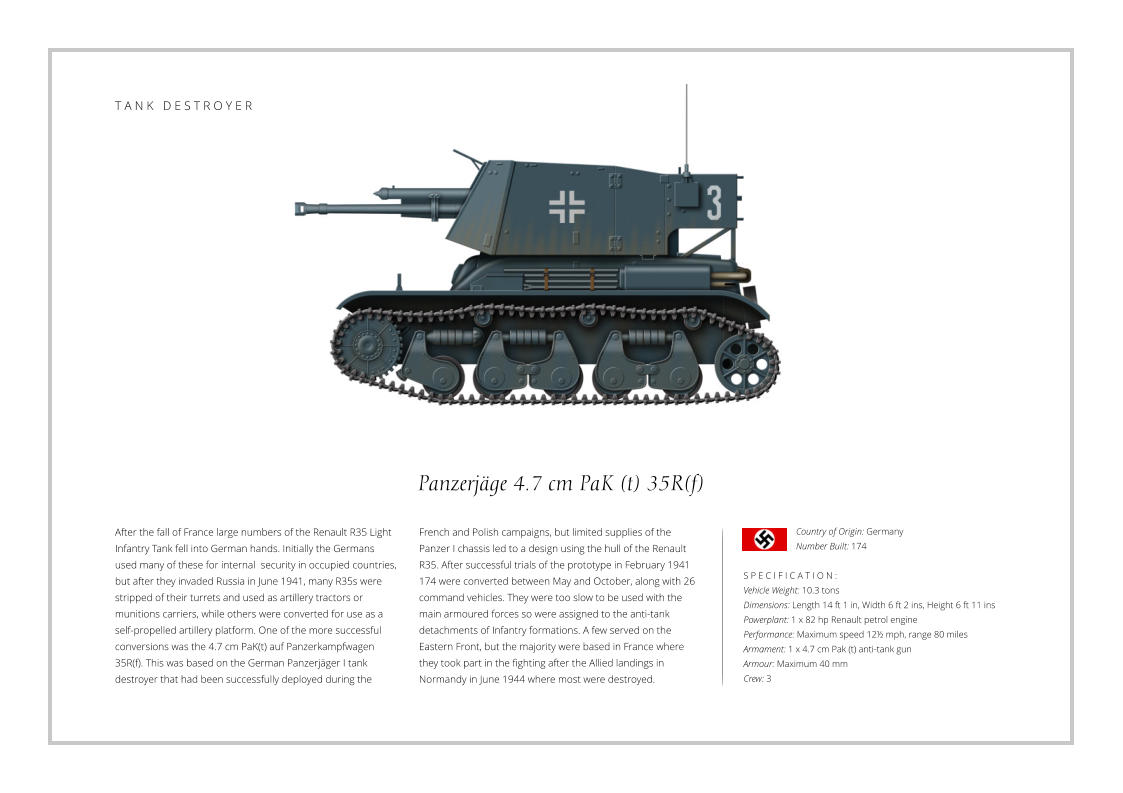
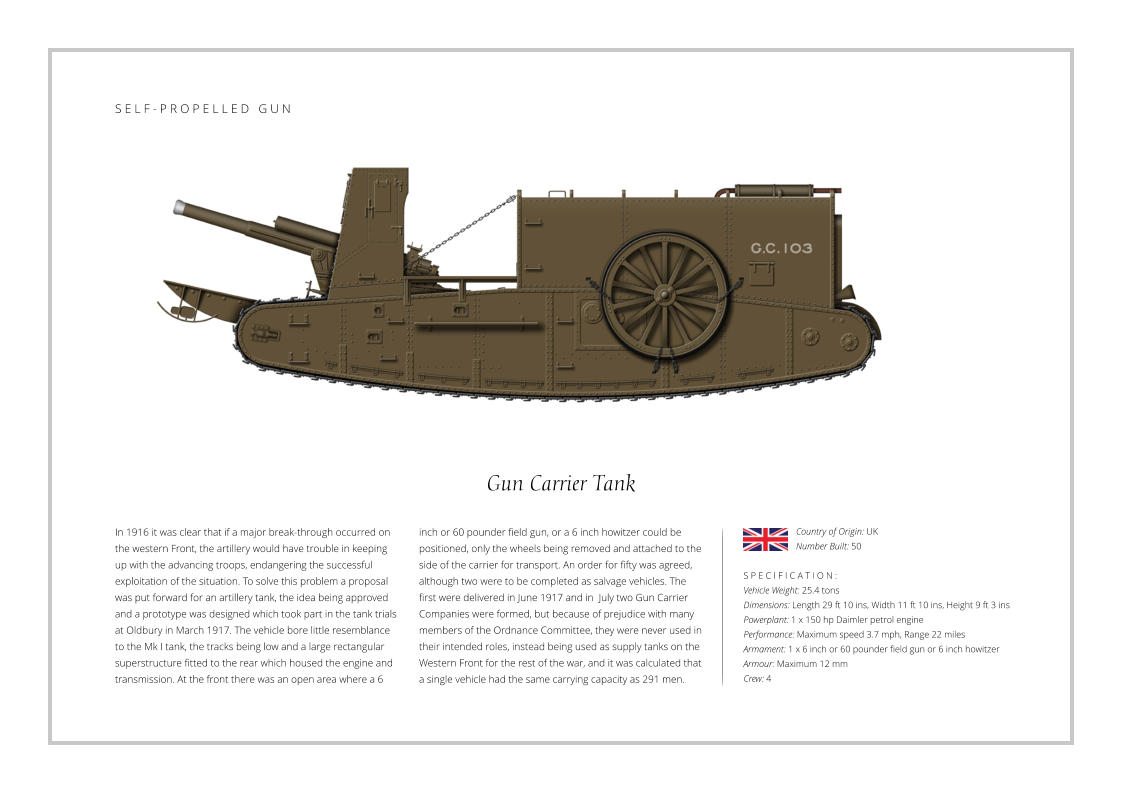
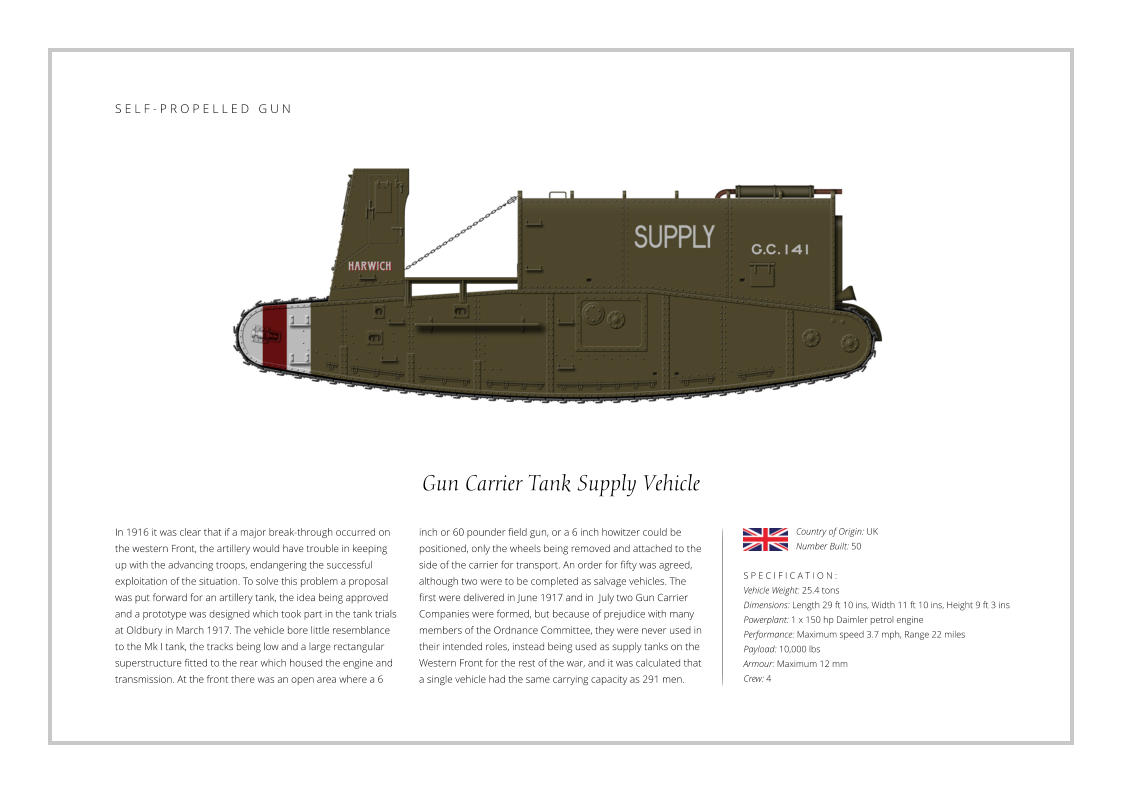
In the early 40’s the U.S. Army developed a strategy to counter
fast moving armoured formations with a tank destroyer force
comprising towed and self-propelled anti-tank guns. The tank
destroyer force were to be used in large formations and armed
with a powerful gun, and one of the first operational vehicles
was the M10 Gun Motor Carriage. The M10 used the chassis of
the M4A2 Sherman tank with a new thinner armoured upper
hull, the armour being sloped to improve effectiveness. The
turret was open topped and also had sloped armour, while the
main gun was a development of a 3 inch anti-aircraft weapon.
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 29.6 tons
Dimensions: Length 22 ft 5 ins, Width 10 ft, Height 8 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 375 hp General Motors diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 32 mph, Range 86 miles
Armament: 1 x 3 inch M7 anti-tank gun,1 x 0.5 inch machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 57 mm
Crew: 5
Production began in September 1942, and when it finished a
year later 4,993 M10s and over 1,400 M10A1s had been built.
The majority of the M10’s were supplied to the US Army and
were first used in action in North Africa after the the Torch
landings in late 1942. Many were also supplied to Britain under
lend-lease who unofficially named it Wolverine, and to make it
more potent, many were re-armed with the new 17 pounder
anti-tank gun, these being known as Achilles. The M10
remained operational until the end of World War Two, by which
time its effectiveness as a tank hunter was nearing its end.
Country of Origin: USA
Number Built: 6,406

T A N K D E S T R O Y E R
























Pages








