
Scroll down to see all the illustrations on the page








Pages




LVT-4 ‘Buffalo’
The LVT-4 was designed in 1943 and based on the previous
LVT-2, and was the first to feature a stern ramp for the loading
and unloading of personnel and cargo. It was also the most
numerous of the LVTs during the World War Two with over
8,300 being built between1943 and 1945. The rear ramp alone
was a remarkable step forward, essentially dictated by early
battle reports over casualties during troop landings. The
vehicle was completely remodelled around this feature, with
the engine relocated from the rear to behind the driver’s cab.
This allowed a larger cargo area and created enough space to
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 16.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 26 ft 1 ins, Width 10 ft 8 ins, Height 8 ft 7 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Continental 250 hp radial engine
Performance: Maximum speed 20 mph, Range 150 miles
Armament: 1 x 20 mm cannon, 3 x 7.62 mm machine guns
Armour: Maximum thickness 13 mm
Crew: 2 • Payload: 9,000 lb or 18 fully equipped troops
accommodate up to 30 troops and also eased loading and
provided better protection to landing forces. The track were
fitted with grousers which propelled the vehicle both on land
and water. The LVT-4 was first used by the Americans in the
Pacific in the summer of 1944 during the landings on Saipan in
June, and Guam and Tinian in July. The British received 500
under Lend-Lease who replaced the 0.5 inch machine gun with
a 20 mm Polsten cannon, and with Canadian forces the LTV-4
played an important part during the Battle of the Scheldte and
the fighting on Walcheren Island in October 1944.
Country of Origin: USA
Number Built: 8,300+
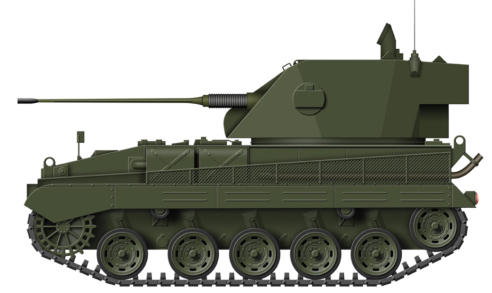
Skink Anti-Aircraft Tank
The development of a fully enclosed quadruple 20 mm mount
on the chassis of the Grizzly tank, (the Canadian built version of
the M4A1 Sherman tank) was approved by the Canadian Army
in March, 1943, and given the name Skink, Ontario's only lizard.
Originally it was planned to arm the Skink with four 20 mm
Hispano-Suiza cannons, but in January 1944 it was decided to
use British 20 mm Polsten gun which required a redesign of
the turret. This was completed in April, but had delayed the
project by 3 to 4 months, while 21st Army Group's reduction in
the number of AA guns it required was drastically reduced,
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 28.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 19 ft 1 ins, Width 8 ft 7 ins, Height 9 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 350 hp Continental radial petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 24 mph, Range120 miles
Armament: 4 x 20 mm Polsten cannons
Armour: Maximum 50 mm
Crew: 4
while the threat from the Luftwaffe had dwindled to almost
nothing in late July 1944, with the Allies enjoying absolute air
superiotity over North West Europe. As there was no longer a
requirement for self-propelled anti-aircraft guns, the Skink
contract was cancelled in mid August after only three complete
vehicles and eight turret kits had been completed. In February
and March 1945 the Skink was trialled in Europe and often
used against German ground targets where Canadian forces
found it a valuable asset, although no enemy aircraft presented
itself to the Skink's guns, its main purpose for existence.
Country of Origin: Canada
Number Built: 3
Crusader III, AA Mk I
With the A15 Crusader tank being phased out of front line
service from late 1943, a source of chassis became available
that could be used for other purposes. With the larger size of
the Crusader compared to previous withdrawn tanks, a larger
weapon could be mounted, and trials were soon carried out to
mount an anti-aircraft gun on redundant vehicles. The first was
the Crusader AA Mk I, which was a simple conversion in which
the turret was replaced replaced with a 40mm Bofors Anti-
Aircraft gun, complete with its field mount and shield, and it
was in this form that they mainly served in Europe after the D-
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 19.3 tons
Dimensions: Length 19 ft 7 ins, Width 9 ft 1 ins, Height 7 ft 4 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Nuffield 340 hp V12 Liberty engine
Performance: Maximum speed 27 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 40 mm Bofors anti-aircraft gun, 1 x 7.62 mm mg
Armour: Maximum thickness 51 mm
Crew: 4
Day landings in June 1944. Later modifications to the Mk I
incorporated an autoloader and powered mounting, the gun
being mounted in a light armoured turret. The Crusader AA
Mk II had a fully enclosed turret which was armed with a twin
20 mm Oerlikon cannon mount. The Crusader AA Mk III was
similar to the Mk II, the changes being primarily the internal
layout of the turret. By the time they arrived in Europe the
need for such vehicles was negligible due to overwhelming
Allied air superiority, and were mainly used for the defence of
airfields, storage facilities and communication centres.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: Unknown
Mk IX Infantry Carrier
During the first actions of World War One involving tanks, it
became clear that the infantry had difficulty in keeping pace,
not because the soldiers were too slow, as the early tanks
themselves could only move at a walking pace, but because of
enemy machine gun fire. Positions gained at high cost would
be lost for lack of infantry to consolidate the area. In mid 1917
a specification for an armoured vehicle to transport troops was
issued. Initially the vehicle was requested to be capable of
being fitted with sponsons, so it could be turned into a tank,
but this was soon dropped, and what emerged was the worlds
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 26.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 31 ft 11 ins, Width 8 ft 3 ins, Height 8 ft 8 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 150 hp Ricardo petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 4 mph, Range 20 miles
Armament: 2 x 7.7 mm machine guns
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 4 • Payload: 30 troops or 10 tons of stores
first true Armoured Personnel Carrier. As there was no time for
a completely new design, the Mark IX was based on the Mark V,
with the hull lengthened to 31 ft 10 inches. An inner space 13 ft
long by 8 ft wide was created which was enough room for thirty
soldiers or ten tons of cargo. Two prototypes were built which
was followed by an order for 200 in early 1918, but production
difficulties meant that the first Mk IX did not reach France until
October 1918. They appeared too late to be used in World War
One and after the Armistice was signed in November the order
for the remaining vehicles was cancelled.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 34
Ram ‘Kangeroo’
In July 1944 during the fighting shortly after D-Day, the First
Canadian Army became concerned about manpower shortages
due to combat losses. Along with the British, Canadian forces
had received a number of American M3 Half-track APCs, but
the needs of the American army heavily reduced the supply of
the vehicles to their allies. A number of different types of
armoured vehicles were available in the U.K. for conversion
into an APC, which included Ram tanks, with the ‘Ram
Kangaroo’ being one such development. The turret and
ammunition storage was removed and bench seats fitted
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 24.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 9 ft, Width 9 ft 10 ins, Height 8 ft 9 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Continental 400 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 25 mph, Range 145 miles
Armament: 1 x 0.30 inch or 1 x 0.50 inch machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 87 mm
Crew: 2 + 11 troops
within the hull, the now exposed turret ring being the main way
the troops embarked and disembark from the vehicle. They
were designed to carry 11 fully equipped troops, but it was
common practice to cram as many as possible inside , while
others would ride on the outside. The crew of two were located
in a separate compartment, the second crew member
operating the hull machine gun which could be supplemented
by another mounted on the turret ring . The Ram Kangaroo
were first used during the assault of Le Havre in September,
and remained in use with Allied forces well after the war.
Country of Origin: Canada
Number Produced: 500+
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R


Vickers Light Tank AA Mk I/II
The effect of German air power in France and the Low
Countries during May 1940 led to the hasty development of AA
tanks to counter this threat. In late 1949 a number of Mk VIA
and VIB light tanks were soon modified to mount a small turret
fitted with four 7.92 mm Besa machine guns in tandem. Four of
these tanks would then be attached to the regimental HQ
squadron of each British armored regiment for air defence. The
early model was designated Light Tank AA Mk I which was
based on the chassis of a Vickers Light Tank Mk VIA chassis.
This was soon superceded by the Light Tank Mk II which was
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 4.8 tons
Dimensions: Length 13 ft, Width 6 ft 10 ins, Height 7 ft 4 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Meadows 88 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 32 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 4 x 7.92 mm Besa machine guns
Armour: Maximum thickness 12 mm
Crew: 2
based on the VIB Chassis. The vehicles had a crew of two and
were fitted with a redesigned turret that had a mount for four
7.92 mm Besa machine guns or two 15 mm Besa heavy
machine-guns. The early vehicles had manual traverse for the
turret which limited the speed and effectiveness of the system,
but with the Mk II power traverse for the turret was installed,
while improvements to the turret included a better sighting
arrangement and extra stowage space in the rear. They were
first used operationally in North Africa. Production numbers of
these vehicles is unknown and ended in early 1941.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: Unknown


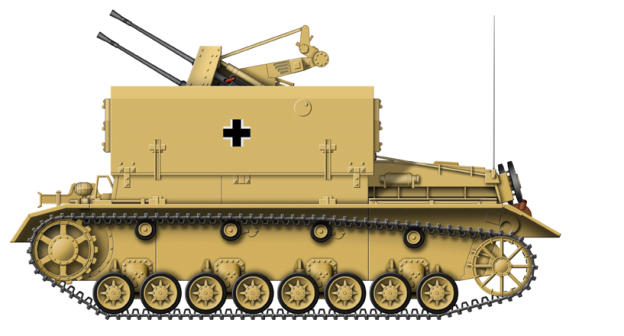
3.7 cm Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen
In the spring of 1943 a Flakpanzer was designed using the
chassis of the Panzer IV medium tank. Originally the vehicle
was designed to be armed with a twin 3.7 cm AA mount in a
protected housing, but Instead a much simpler version was
produced using existing gun mounts on a standard Panzer IV
Ausf H or J hull, the gun being protected with 10 mm hinged
armoured flaps. Known as the Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen, they
looked useful, but in operation were severely handicapped as
the armoured flaps had to be lowered flat to give a clear
traverse for the armament and sufficient working space for the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 24 tons
Dimensions: Length 21 ft 9 ins, Width 9 ft 5 ins, Height 8 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Maybach 300 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 24 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 3.7 cm Flak 43 AA gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 80 mm
Crew: 6
gun crew leaving them totally unprotected. With the flaps
raised, the Mobelwagen had a high silhouette which made it
hard to conceal. 240 were produced which used two different
gun mounts, one version having the 2 cm Flakvierling 38
quadruple mount, while the other had a single 3.7 cm Flak 43.
The Möbelwagen entered service in the autumn 1943 and were
issued to the AA platoons of tank regiments until the end of
1944. The shortcomings of the design were well known by the
military, and by December 1943 a replacement design was
approved with a fully traversing armoured gun housing.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 240
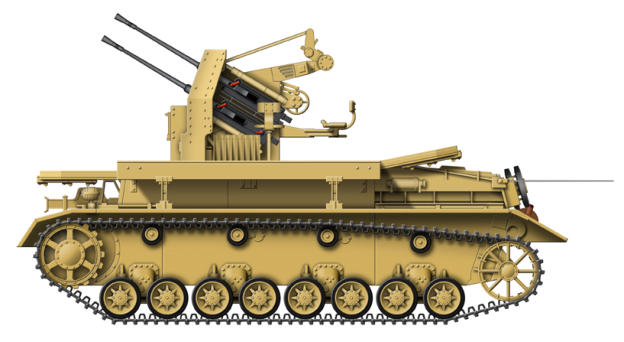
2 cm Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen
In the spring of 1943 a Flakpanzer was designed using the
chassis of the Panzer IV medium tank. Originally the vehicle
was designed to be armed with a twin 3.7 cm AA mount in a
protected housing, but Instead a much simpler version was
produced using existing gun mounts on a standard Panzer IV
Ausf H or J hull, the gun being protected with 10 mm hinged
armoured flaps. Known as the Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen, they
looked useful, but in operation were severely handicapped as
the armoured flaps had to be lowered flat to give a clear
traverse for the armament and sufficient working space for the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 24 tons
Dimensions: Length 21 ft 9 ins, Width 9 ft 5 ins, Height 8 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Maybach 300 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 24 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 2 cm Flakvierling quadruple mount
Armour: Maximum thickness 80 mm
Crew: 6
gun crew leaving them totally unprotected. With the flaps
raised, the Mobelwagen had a high silhouette which made it
hard to conceal. 240 were produced which used two different
gun mounts, one version having the 2 cm Flakvierling 38
quadruple mount, while the other had a single 3,7 cm Flak 43.
The Möbelwagen entered service in the autumn 1943 and were
issued to the AA platoons of tank regiments until the end of
1944. The shortcomings of the design were well known by the
military, and by December 1943 a replacement design was
approved with a fully traversing armoured gun housing.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 240
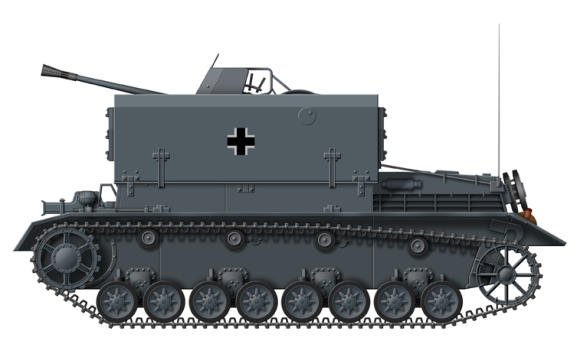
3.7 cm Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen
In the spring of 1943 a Flakpanzer was designed using the
chassis of the Panzer IV medium tank. Originally the vehicle
was designed to be armed with a twin 3.7 cm AA mount in a
protected housing, but Instead a much simpler version was
produced using existing gun mounts on a standard Panzer IV
Ausf H or J hull, the gun being protected with 10 mm hinged
armoured flaps. Known as the Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen, they
looked useful, but in operation were severely handicapped as
the armoured flaps had to be lowered flat to give a clear
traverse for the armament and sufficient working space for the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 24 tons
Dimensions: Length 21 ft 9 ins, Width 9 ft 5 ins, Height 8 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Maybach 300 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 24 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 3.7 cm Flak 43 AA gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 80 mm
Crew: 6
gun crew leaving them totally unprotected. With the flaps
raised, the Mobelwagen had a high silhouette which made it
hard to conceal. 240 were produced which used two different
gun mounts, one version having the 2 cm Flakvierling 38
quadruple mount, while the other had a single 3,7 cm Flak 43.
The Möbelwagen entered service in the autumn 1943 and were
issued to the AA platoons of tank regiments until the end of
1944. The shortcomings of the design were well known by the
military, and by December 1943 a replacement design was
approved with a fully traversing armoured gun housing.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 240
Falcon Anti-Aircraft Vehicle
Developed in the late-1960s, the ‘Falcon’ was a Self-Propelled
Anti-Aircraft Gun (SPAAG) system based on the hull of the
‘Abbot’ self-propelled gun. A new two man powered turret was
designed that was armed with two stabilised 30 mm Hispano
Suiza auto-cannons which had a rate of fire of 1,300 rounds
per minute and a range of 10,000 ft. To ease logistics they used
the same ammunition as the British built 30 mm Rarden
cannon that was used on the Scimitar and Fox light armoured
vehicles. The Falcon was designed with a crew of three, the
commander, gunner, and driver, and was primarily intended to
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 16.3 tons
Dimensions: Length 20 ft, Width 8 ft 6 ins, Height 8 ft 2 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 1 x Rolls-Royce 240 hp multi-fuel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 29 mph, Range 300 miles
Armament: 2 x 30 mm Hispano Suiza auto-cannons
Armour: Maximum 12 mm
Crew: 3
combat aircraft over the battlefield, although it was highly
effective against lightly armoured vehicles. A prototype was
produced in the early 1970s and extensively trialled, and
although these proved successful the vehicle did not receive
favourable opinions from military officials. The main reason for
this was largely due to a rather small ammunition capacity the
vehicle could carry. This was due to the cramped nature of the
hull, and in action would have required support vehicles to
keep the Falcon operational, while the lack of a radar guidance
system for the guns led the the termination of the project.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 1
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R
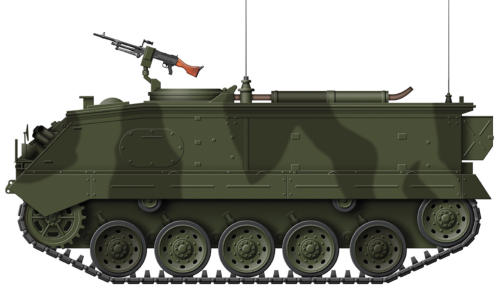
M9 Halftrack Personnel Carrier
The development of the American halftrack started in the
1920s, when a number of Citroen-Kegresse halftracks were
purchased from France. The U.S. military put into effect a long
series of development models before the hull of the White
Scout Car M2 was mated with a Kegresse halftrack suspension
which emerged as the Half-Track Car M2 that was put into
production in early 1941. From then on halftracks rolled off the
assembly lines in their thousands, most being personnel
carriers for the infantry, but the vehicle was adapted for a
multitude of roles and all manner of experimental types. After
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 8.4 tons
Dimensions: Length 20 ft 7 ins, Width 7 ft 3 ins, Height 7 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x International Harvester 141 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 42 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 0.5 inch and 2 x 0.30 inch machine guns
Armour: Maximum thickness 16 mm
Crew: 3 + 10 fully equipped troops
the U.S. entered the war in December 1941, the urgent need
for mobile artillery saw many halftrack being armed with a wide
variety of weapons such as the 57 mm anti-tank gun, a 75 mm
field gun, and even a 105 mm howitzer. Later developments
were anti-aircraft versions armed with multiple machine-guns,
20 mm cannon and 40 mm Bofors guns. It was however as a
personnel carrier that were the mostly used. The design was
developed throughout World War Two, with total production of
all types being over 76,000 vehicles, and were used by most
allied nations and continued in service for many years.
Country of Origin: USA
Number Produced: 3,500
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R

Flakpanzerwagen I Ausf A
During the French Campaign in 1940, it became clear to the
High Command of the German Army that their motorised Flak
vehicles were insufficiently armoured. As a consequence it was
decided to combine light anti-aircraft guns with tank chassis,
and the obvious choice for conversion was the Panzer I. Parts
of the superstructure were removed and the engine compart-
ment rearranged to provide standing room, while flaps on the
side folded down to provide extra space for the crew when in
action. They were armed with the 20 mm Flak 38, ammunition
being stored inside the vehicle plus a towed trailer with further
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 5.7 tons
Dimensions: Length 13 ft 2 ins, Width 6 ft 8 ins, Height 5 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Krupp M 305 59 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 38 mph, Range 170 miles
Armament: 1 x 20 mm Flak 38 gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 13 mm
Crew: 4
ammunition and replacement barrels. High development costs
limited the construction to just 24 vehicles which were assigned
to Flak Battalion 614 that was formed in 1941. The unit took
part in the invasion of Russia in the south, but the Flakpanzer I
proved to be of little use against aircraft as the gun only had a
limited traverse mount. Instead they were often used against
ground targets in support of other units, but with the vehicles
insufficient protection for the crew they suffered high losses.
The battalion was finally wiped out in 1943 at Stalingrad, by
which time the vehicles had probably already been destroyed.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 24
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
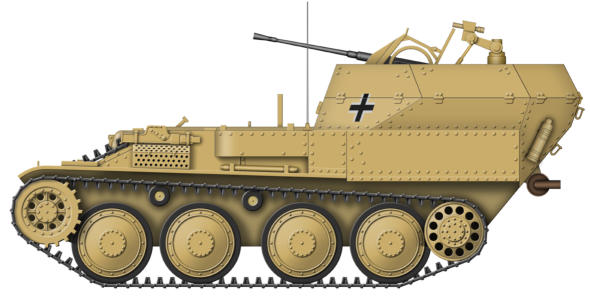
Flakpanzer 38(t)
The Flakpanzer 38(t) was based on the chassis of the pre-war
Czech LT vz 38 light tank which was produced for the German
Army as the Panzer 38(t) following the German occupation. By
early 1943 the light tank was no longer an effective weapon,
but the chassis and running gear was reliable and capable of
adaptation for other uses, one of these being the Flakpanzer
38(t). The Ausf M chassis was used but the engine was moved
to the middle so that the armament could be placed to the
rear of the vehicle in an armoured compartment, the sides of
which could fold down to allow 360 degree traverse at low
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 9.65 tons
Dimensions: Length 15 ft 1 in, Width 7 ft 1 ins, Height 7 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 147 hp Praga petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 26 mph, Range 130 miles
Armament: 1 x 20 mm Flak 38 gun
Armour: Maximum 15 mm
Crew: 4
elevation. Between November 1943 and February 1944 141
were built which included the prototype, which entered service
in the spring of 1944. The Flakpanzer 38(t) was intended to be
issued to the anti-aircraft platoon of each tank battalion in a
Panzer division, most vehicles being issued to Panzer Divisions
in the west, the remainder being issued to units on the Eastern
Front. By 1944 the single 2 cm FlaK gun was no longer an
effective anti-aircraft weapon, but as its folding superstructure
allowed a very low elevation the Flakpanzer 38(t) was often
used against enemy infantry and other ground targets.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 141
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
2 cm Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen
In the spring of 1943 a Flakpanzer was designed using the
chassis of the Panzer IV medium tank. Originally the vehicle
was designed to be armed with a twin 3.7 cm AA mount in a
protected housing, but Instead a much simpler version was
produced using existing gun mounts on a standard Panzer IV
Ausf H or J hull, the gun being protected with 10 mm hinged
armoured flaps. Known as the Flakpanzer IV Mobelwagen, they
looked useful, but in operation were severely handicapped as
the armoured flaps had to be lowered flat to give a clear
traverse for the armament and sufficient working space for the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 24 tons
Dimensions: Length 21 ft 9 ins, Width 9 ft 5 ins, Height 8 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Maybach 300 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 24 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 2 cm Flakvierling quadruple mount
Armour: Maximum thickness 80 mm
Crew: 6
gun crew leaving them totally unprotected. With the flaps
raised, the Mobelwagen had a high silhouette which made it
hard to conceal. 240 were produced which used two different
gun mounts, one version having the 2 cm Flakvierling 38
quadruple mount, while the other had a single 3,7 cm Flak 43.
The Möbelwagen entered service in the autumn 1943 and were
issued to the AA platoons of tank regiments until the end of
1944. The shortcomings of the design were well known by the
military, and by December 1943 a replacement design was
approved with a fully traversing armoured gun housing.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 240







S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N

S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
M44 Gun Motor Carriage
In the early 1950s, experience in Korea led to the U.S. Army
wanting to replace the M41 155 mm Howitzer Motor Carriage
with an improved version better suited to the conditions.
Design of the new vehicle commenced and was based on the
recently introduced M41 Walker Bulldog light tank, giving the
vehicle good mobility. The gun was a version of the M114
howitzer that had been introduced in 1942, and was mounted
in an enclosed armoured gun house that gave the crew better
protection, while a spade was provided at the rear of the
vehicle that could be positioned in the ground to stabilise the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 25.9 tons
Dimensions: Length 24 ft 3 ins, Width 10 ft 8 ins, Height 10 ft 7 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Continental 500 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 35 mph, Range 76 miles
Armament: 1 x 155 mm M80 Howitzer, 1 x 0.5 inch machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 12 mm
Crew: 5
vehicle when the gun was fired. The same chassis, running
gear and engine of the M41 light tank was used which gave the
M44 a speed of 35 mph over good surfaces. Due to the Korean
situation the vehicle was rushed into production before trials
had been completed, but this was halted after 250 had been
built when it was realised that the enclosed design allowed the
build up of dangerous gasses when the gun was fired. This was
solved by removing the roof, but left the crew exposed to the
elements and the dangers of the battlefield. From 1963
onwards they replaced by the M109 self-propelled gun.
Country of Origin: USA
Number Built: 250


S E L F - P R O P E L L E D G U N


3.7 cm Flakpanzer IV ‘Ostwind’
The Flakpanzer IV ‘Ostwind’ (East Wind) was another German
self-propelled anti-aircraft gun based on the Panzer IV tank.
Development began in mid 1944 and was based on the earlier
Flakpanzer IV 2 cm Vierling ‘Wirbelwind’. The Ostwind's main
improvement was the use of the 3.7 cm FlaK 43 anti-aircraft
gun which had a better range and hitting power compared to
the 2 cm Flakvierling 38. The turret was of a simpler design and
better armoured, and at first it was hoped it could be enclosed
to give the gun crew better protection, but the fumes from the
gun made this impractical. 1,000 rounds could be carried
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 26 tons
Dimensions: Length 19 ft 5 ins, Width 9 ft 8 ins, Height 9 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 300 hp Maybach petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 24 mph, Range 124 miles
Armament: 1 x 3.7 cm FlaK 43 anti-aircraft gun
Armour: Maximum 80 mm
Crew: 5
aboard the vehicle, while for local defence against infantry the
hull 7.92 mm machine gun was retained. An order for 100
vehicles was placed in August 1944, but by the end of the war
in May 1945 only 44 had been completed, 37 being converted
from existing Panzer IVs that had returned to Germany for
repairs, and 7 new production vehicles. By the time they
entered service the war in Europe was nearing its conclusion,
but apart from their intended role as an anti-aircraft weapon,
the fast firing 3.7 cm gun also proved to be highly effective
against light vehicles and infantry.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 44
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N





Crusader III, AA Mk II/III
With the A15 Crusader tank being phased out of front line
service from late 1943, a source of chassis became available
that could be used for other purposes. With the larger size of
the Crusader compared to previous withdrawn tanks, a larger
weapon could be mounted, and trials were soon carried out to
mount an anti-aircraft gun on redundant vehicles. The first was
the Crusader AA Mk I, which was a simple conversion in which
the turret was replaced replaced with a 40mm Bofors Anti-
Aircraft gun, complete with its field mount and shield, and it
was in this form that they mainly served in Europe after the D-
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 19.3 tons
Dimensions: Length 19 ft 7 ins, Width 9 ft 1 ins, Height 7 ft 4 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Nuffield 340 hp V12 Liberty engine
Performance: Maximum speed 27 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: 1 x 40 mm Bofors anti-aircraft gun, 1 x 7.62 mm mg
Armour: Maximum thickness 51 mm
Crew: 4
Day landings in June 1944. Later modifications to the Mk I
incorporated an autoloader and powered mounting, the gun
being mounted in a light armoured turret. The Crusader AA
Mk II had a fully enclosed turret which was armed with a twin
20 mm Oerlikon cannon mount. The Crusader AA Mk III was
similar to the Mk II, the changes being primarily the internal
layout of the turret. By the time they arrived in Europe the
need for such vehicles was negligible due to overwhelming
Allied air superiority, and were mainly used for the defence of
airfields, storage facilities and communication centres.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: Unknown


S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N
S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N


S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N





















Pages






S E L F - P R O P E L L E D A A G U N