Scroll down to see all the illustrations on the page








Pages




Raupenschlepper OST (RSO)
After the Germans invaded the Soviet Union in 1941, they
began to experience the full effects of a Russian autumn and
winter. The primitive roads soon became quagmires, and to
maintain the mobility of the army Steyr proposed a small, fully
tracked vehicle based on its 1500A light truck. They were initial
designed as a prime mover and artillery supply vehicle, and
had a pressed steel cab and a wooden drop-side cargo flatbed.
A simple suspension system was used instead of the complex
interleaved wheel arrangement of most German halftracks
which proved better at handling the conditions of the Russian
S P E C I F I C A T I O N : (RS0/01)
Weight: 3 tons
Dimensions: Length 14 ft 6 ins,
Width 6 ft 4 ins, Height 8 ft 4 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 85 hp Steyr petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 18 mph, Range 186 miles
Armament/Armour: None
Crew: 2
winter, where mud or snow could build up between the wheel
arrangement of a halftrack and freeze which would disable the
vehicle. Named the Raupenschlepper Ost they entered service
in 1942, and although designed as a prime mover they were
soon used for general duties and a wide variety of other roles,
including an ambulance and communication vehicles. To meet
demand new versions appeared. The RSO/2 introduced a new
flat sided cab that was cheaper and easier to produce, while
the RSO itself became one of the workhorses on the eastern
front, and in total over 28,000 were built.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 28,000+
Loyd Carrier
In 1939, Captain Vivian Loyd developed a simple cross-country
vehicle which was primarily built from off the shelf parts from
various manufacturers. The main components for the vehicle
were the chassis, engine, gearbox and rear axle from the Ford
2 ton truck which were combined with the suspension and
tracks from the Vickers light tank. The vehicle was open topped
but was issued with a canvas tilt to give the crew protection in
bad weather. The vehicle was trialled by the army and accepted
for production, with an initial order for 200 vehicles being
placed in early 1939. These first vehicles were fitted with
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 4.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 13 ft 11 ins, Width 6 ft 9 ins, Height 4 ft 8 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 85 hp Ford V8 petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 30 mph, Range140 miles
Armament: None
Armour: 7 mm
Crew: 1 + gun crew
armoured panels and could carry up to ten men, however, the
majority of the 26,000 Loyd Carriers produced were of the five
seat towing version which were fitted with ammunition stowage
racks over the track guards. They were mainly used for towing
the 6 pounder anti-tank gun or the 4.2 inch mortar, and when
towing the 6 pounder they usually operated in pairs, one for
the gun and its crew, and the other carrying the ammunition.
Although heavily criticised for its performance, the Loyd carrier
remained in service throughout World War Two, but was rapidly
phased out of British service during the late 1940s.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 26,000
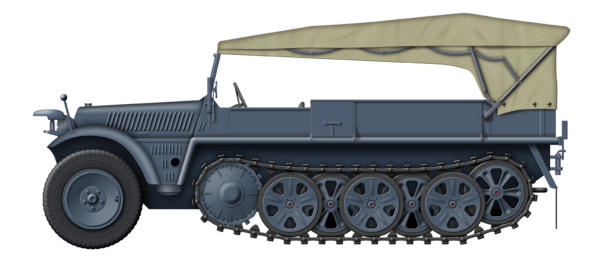
Demag SdKfz 10
Design work on the Demag SdKfz 10 series of half-tracks began
in 1934, initially under the guise of a commercial product to
circumvent the terms of the Versaille Treaty. Drive was only
provided to the tracks, the front wheels being non-powered
meant that steering could become difficult in soft terrain. The
suspension was of the torsion bar type and gave the vehicle a
ground clearance of 13 inches (33 cm), which aided the
vehicles good off-road performance, even over uneven terrain.
They had a maximum speed of 47 mph per hour and an
operational range of 190 miles over good surfaces. They were
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Weight: 3.37 tons
Dimensions: Length 15 ft 6 ins, Width 6 ft 3 ins, Height 6 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Maybach 99 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 40 mph, Range 190 miles
Armament: None
Armour: None
Crew: 2 + 6 passengers
classified as a lightweight half-track and were given an official
towing capacity of 1 ton, and were intended as an artillery
tractor for light calibre artillery weapons like the 2 cm FlaK 30
anti-aircraft gun up to the lightweight 7.5 cm leIG infantry
support gun. Full scale production began in 1938, with the
SdKfz 10 being seen in many guises during its career. The SfKfz
10/4 mounted the 2 cm FlaK 30 anti-aircraft gun system on a
flatbed, while the SdKfz 10/5 had the faster-firing 2 cm FlaK 38
gun instead. Both of these models featured fold-down panels
that acted as a platform for the gun crew when in action.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Produced: 14,000+
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R


Medium Dragon Mk IV
In 1930 Vickers produced a medium gun tractor based on their
‘6 Ton Tank’ design that had successfully been sold abroad but
failed to find an order from the British army. One machine was
purchased for evaluation, but was rejected on the grounds of
being underpowered. In 1934 Vickers uprated the design with
a more powerful engine, and after a further assessment were
rewarded with an order for twelve tractors from the British
military. These were designated the Medium Dragon Mk IV
and were all allotted to one of the heavy artillery regiments. In
1939 they were part of the British Expeditionary Force sent to
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 8 tons
Dimensions: Length 15 ft, Width 7 ft 11 ins, Height 6 ft 10 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Armstrong-Siddeley 115 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 20 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: None
Armour: Maximum thickness 13 mm
Crew: 2 + gun crew
France, and during the fighting in 1940 they were either all
destroyed or captured before the B.E.F. was evacuated from
Dunkirk. Further vehicle were purchased by foreign powers,
and included China who purchased twenty-three in 1935 and
India who acquired eighteen in 1937, while Both Russia and
Poland produced similar vehicles based on their version of the
Vickers 6 ton tank. The chassis was also developed by Vickers
into a self-propelled anti-aircraft gun system. This had an open
superstructure that mounted a 40 mm pom-pom anti-aircraft
gun, twenty-six being produced for Siam.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 65
Loyd Carrier
In 1939, Captain Vivian Loyd developed a simple cross-country
vehicle which was primarily built from off the shelf parts from
various manufacturers. The main components for the vehicle
were the chassis, engine, gearbox and rear axle from the Ford
2 ton truck which were combined with the suspension and
tracks from the Vickers light tank. The vehicle was open topped
but was issued with a canvas tilt to give the crew protection in
bad weather. The vehicle was trialled by the army and accepted
for production, with an initial order for 200 vehicles being
placed in early 1939. These first vehicles were fitted with
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 4.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 13 ft 11 ins, Width 6 ft 9 ins, Height 4 ft 8 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 85 hp Ford V8 petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 30 mph, Range140 miles
Armament: None
Armour: 7 mm
Crew: 1 + gun crew
armoured panels and could carry up to ten men, however, the
majority of the 26,000 Loyd Carriers produced were of the five
seat towing version which were fitted with ammunition stowage
racks over the track guards. They were mainly used for towing
the 6 pounder anti-tank gun or the 4.2 inch mortar, and when
towing the 6 pounder they usually operated in pairs, one for
the gun and its crew, and the other carrying the ammunition.
Although heavily criticised for its performance, the Loyd carrier
remained in service throughout World War Two, but was rapidly
phased out of British service during the late 1940s.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 26,000
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R
Medium Dragon Mk II
After the tank's success in World War One, the British Army
took an interest in developing a tracked towing vehicles for the
artillery. In 1924, the Royal Ordnance Factory at Woolwich
began to build such a vehicle using the track and suspension
units of the Vickers medium tank. The vehicle could carry 11
men including the driver, and was intended to tow the 18
pounder field gun and limber, which was the standard field gun
of the British Army at the time. Eighteen were built and named
Medium Dragon, (it is believed the name is derived from their
function, 'drag gun'), but they proved to be under-powered and
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 4.6 tons
Dimensions: Length 15 ft, Width 7 ft 11 ins, Height 5 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 90 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 20 mph, Range 125 miles
Armament: None
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 2 + 8 passengers
too slow for their intended role and were soon relegated to the
training role. A number of modifications were introduced on
the Medium Dragon Mk II which included a more powerful a 90
engine, the layout of the interior and seating was improved,
provisions for a bad weather coverall for the driver and
passengers, while the ammunition boxes were relocated to the
sides of the vehicle that opened outwards which allowed easier
access for the gun crew. Only 28 Mk IIs were built, but these
were supplemented by 12 Mk IIIs which were uprated to
permit them to tow the 60 pounder or 6 inch field howitzer.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 28
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R
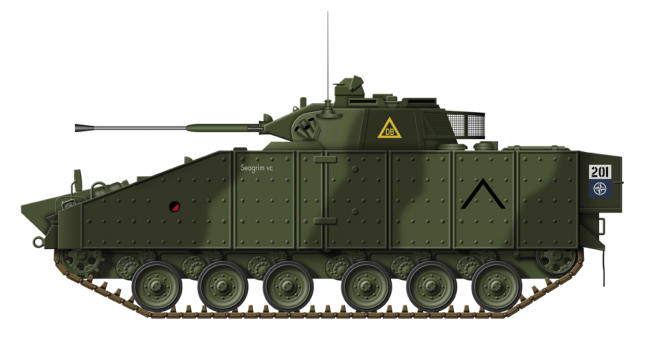
FV103 ‘Spartan’
The FV103 Spartan was developed in the 1970s as the
Armoured Personnel Carrier version of the CVR(T) family.
Designed by Alvis, the Spartan entered service with the British
Army in 1978, and is similar in appearance to the missile
armed FV102 Striker. The Spartan can carry seven soldiers in
a combination of 2/3 crew and 4/5 passengers, with its main
function being the transportation of small specialised groups
such as reconnaissance teams and fire controllers. In addition
to its APC role, it has also been used as a resupply vehicle for
the FV102 Striker, carrying extra Swingfire anti-tank missiles. An
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 9 tons
Dimensions: Length 16 ft 9 ins, Width 8 ft 2 ins, Height 8 ft 8 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Jaguar 190 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 50 mph, Range 400 miles
Armament: 1 x 7.62 mm machine
Armour: Maximum thickness 12.5 mm
Crew: 2/3 + 4/5 passengers
anti-tank version of the FV103 was also produced that was
named the FV120 Spartan MCT (Spartan with MILAN Compact
Turret). This version was fitted with a turret armed with two
MILAN missiles with a further eleven carried internally. Later
production vehicles of the Spartan had a number of
improvements, which included an uprated suspension and the
replacement of the Jaguar petrol engine with a more efficient
Perkins diesel engine. By 1995 over 960 had been built for
both the home and export market, but from 2009 have been
gradually withdrawn from service with British forces.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 960
FV104 ‘Samaritan’
The FV104 Samaritan is the armoured ambulance member of
the CVR(T), which outwardly resembles the Sultan command
vehicle, except it is unarmed. The Samaritan has a crew of two
and is capable of taking up to six walking wounded or three
stretcher cases, and with its speed, agility and relatively low
profile is an ideal MEDEVAC system. Other members of the
CVR(T) family included the FV105 Sultan, which is a British Army
command vehicle. It has a higher roof than the Spartan APC
which provides space inside for a large vertical map board and
desk along one side, with a bench seat for three people. Ahead
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 8.7 tons
Dimensions: Length 16 ft 9 ins, Width 8 ft 2 ins, Height 8 ft 8 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Jaguar 190 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 50 mph, Range 400 miles
Armament: None
Armour: Maximum thickness 12.5 mm
Crew: 2 + up to 6 casualties
of this are positions for the radio operator and vehicle
commander, whose seat can be raised to give him access to
the pintle-mounted machine gun. The driver sits forward of this
in a small compartment beside the engine space. The back of
the vehicle is designed to be extended by an attached tent to
form a briefing area. The final member of the family is the The
FV106 Samson armoured recovery vehicle. The hull was
adapted to contain a winch which is positioned to the rear of
the vehicle. This winch could also be utilised in a lifting
configuration and is capable of recovering a 12 ton load.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: Unknown

FV4333 'Stormer’
The Stormer has its origins in the late 1970s as a development
of the Scorpion CVR(T) family, and was primarily designed for
the export market. In the 1970s the manufacturing and
marketing rights of the FV4333 was purchased by Alvis from
the British Ministry of Defence. The vehicle was based on the
Spartan APC, and to increase internal space the hull was
lengthened which required an additional roadwheel each side
for better weight distribution and drive performance. The basic
shape of the CVR(T) family was largely retained with many of
the proven components of the CVR(T) being used, although the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 12.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 17 ft 6 ins, Width 8 ft 10 ins, Height 7 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Perkins 250 hp diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 50 mph, Range 400 miles
Armament: Normally 1 x 7.62 mm machine gun
Armour: Not available
Crew: 3 • Payload: 8 troops and their equipment
Jaguar petrol engine was replaced by a turbocharged Cummins
or Perkins diesel engine. The vehicle usually had a crew of two
and could carry a maximum of nine troops, while a wide range
of weapons could be also be mounted on the roof depending
on its selected role. Designated Stormer the first prototype
appeared in 1978 with production beginning in 1981. The
British Army received at least 150, while export sales included
25 for Malaysia, 40 for Indonesia and 4 to Oman. The Stormer
has been adapted for a variety of roles, and marketed in many
combinations of armament depending on its intended role.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 250+

Windsor Carrier
As World War Two progressed, the need for larger anti-tank
weapons in infantry and anti-tank units became urgent, along
with a carrier capable of hauling them and their ammunition.
The Windsor Carrier was a Canadian design based on the
British Universal Carrier, but lengthened by 28 inches to
accommodate two twin bogie sets on each side that provided
more stability. Compared to the Universal Carrier the Windsor
was just over 1 ton heavier, and to compensate for the extra
weight they had a more powerful engine. The Windsor still used
the combination of track warping and brakes for steering, but
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 4.65 tons
Dimensions: Length 14 ft 4 ins, Width 6 ft 9 ins, Height 2 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Ford 115 hp V8 petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 30 mph, Range 150 miles
Armament: 1 x Bren light machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 3
other changes included the provision for a canvas cover to
protect the crew in bad weather and a revised internal layout.
In total 5,000 vehicles were produced by Fords of Canada
during 1944-45 and were mainly used as a tractor for the 6
pounder anti-tank gun with Canadian units in north-west
Europe. A similar vehicle was also produced by Fords in the
United States which were supplied to Canadian forces under
the Lend Lease agreement. Known as the T16, they was not as
long, and Instead of the track warping used brakes to slow
individual tracks to steer the vehicle.
Country of Origin: Canada
Number Built: 5,000
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R

Voroshilovets Prime Mover
Work on a new heavy prime mover for the Soviet army began
in 1935. The vehicle was fully tracked, and was developed as a
more powerful alternative to the Komintern prime mover. The
Voroshilovets used the suspension and running gear of the
T24 tank that had entered service in small numbers during
1931, and were initially powered by a 400 hp diesel engine, this
later being changed to a 375 hp V2V diesel engine, a detuned
version of the engine used in the T34 tank. The Voroshilovets
was the largest of the Russian tracked artillery tractors with a
towing capacity of 22 tons, and was used as the prime mover
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Weight: 15.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 20 ft 5 ins, Width 7 ft 8 ins, Height 9 ft
Powerplant: 1 x 375 hp diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 22 mph, Range 167 miles
Armour: None
Crew: 2 + 16 man gun crew
Payload: 3 tons • Towing Capacity: 22 tons
for heavy artillery such as the B4 203 mm tracked howitzer and
the Br5 280 mm heavy mortar. They had a crew of two and
seating for a 16 man gun crew or 3 tons of cargo in the rear
flatbed area which could be fitted with a storm cover in bad
weather. They began to enter service in 1939, and by the time
of the German invasion in 1941 about 230 had been built. In
late 1941 the factory at Kharkov was evacuated and production
transferred to the Stalingrad Tractor Factory. More than 1,100
had been built when production came to end in the autumn of
1942 after the factory was overrun by the Germans.
Country of Origin: USSR
Number Built: 1,100+
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R

FV510 ‘Warrior’
The Warrior Armoured Infantry Fighting Vehicle was designed
in the late 1970s as a replacement for the FV432 armoured
personnel carrier that had been in service with the British Army
since the early 1960s. A prototype was ready in 1980, followed
by a further eleven which were successfully trialled, one being
demonstrated in the Middle East which led to the development
of a dedicated Desert Fighting Vehicle. The British Government
placed an order for the 290 vehicles in 1984, 170 being fitted
with a two man turret armed with a 30 mm RARDEN cannon,
with the remainder being specialised variants. Production
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 25 tons
Dimensions: Length 20 ft 8 ins, Width 9 ft 11 ins, Height 9 ft 2 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Perkins 550 hp diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 46 mph, Range 410 miles
Armament: 1 x 30 mm cannon, 1 x 7.62 mm chain gun
Armour: Not available
Crew: 3 + 7 troops and their equipment
began in January 1986, with the first vehicles being handed
over to the British Army in May 1987, and by mid 1988 were in
service at Battalion level with the British Army of the Rhine. The
crew of the Warrior comprises a driver, who is positioned in the
front hull, and the gunner and commander who are both in the
turret. An infantry section of up to seven fully equipped soldiers
can be carried who in the rear hull compartment, access being
provided by a door at the rear of the hull. In total 789 have
been built for the British Army, many being deployed in both
Gulf Wars, Afghanistan and with United Nation forces.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 1,000+s

FV510 ‘Warrior’
The Warrior Armoured Infantry Fighting Vehicle was designed
in the late 1970s as a replacement for the FV432 armoured
personnel carrier that had been in service with the British Army
since the early 1960s. A prototype was ready in 1980, followed
by a further eleven which were successfully trialled, one being
demonstrated in the Middle East which led to the development
of a dedicated Desert Fighting Vehicle. The British Government
placed an order for the 290 vehicles in 1984, 170 being fitted
with a two man turret armed with a 30 mm RARDEN cannon,
with the remainder being specialised variants. Production
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 25 tons
Dimensions: Length 20 ft 8 ins, Width 9 ft 11 ins, Height 9 ft 2 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Perkins 550 hp diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 46 mph, Range 410 miles
Armament: 1 x 30 mm cannon, 1 x 7.62 mm chain gun
Armour: Not available
Crew: 3 + 7 troops and their equipment
began in January 1986, with the first vehicles being handed
over to the British Army in May 1987, and by mid 1988 were in
service at Battalion level with the British Army of the Rhine. The
crew of the Warrior comprises a driver, who is positioned in the
front hull, and the gunner and commander who are both in the
turret. An infantry section of up to seven fully equipped soldiers
can be carried who in the rear hull compartment, access being
provided by a door at the rear of the hull. In total 789 have
been built for the British Army, many being deployed in both
Gulf Wars, Afghanistan and with United Nation forces.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 1,000+

A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R

Light Dragon Mk II
Another line of artillery tractors from Vickers were based on
their series of light tanks. The Light Dragon Mk II was based on
the chassis and suspension of the Light Tank Mk II which had
entered service with the British Army in small numbers during
the early 1930s. Seats were provided for a gun crew of six to
the rear, with ammunition being stored in the central area of
the vehicle. After trials the vehicle was accepted for service with
the British army who would use it for towing weapons such as
the 18 pounder field gun and 4.5 inch howitzer. The Light
Dragon Mk II began to enter service in 1931, and was followed
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 3.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 13 ft 2 ins, Width 6 ft 1 in, Height 5 ft 7 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Meadows 58 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 32 mph, Range 160 miles
Armament: None
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 2 + gun crew
by the Mk IIA, Mk IIB, Mk IIC and Mk IID, the Mk IIC introducing a
revised Horstmann suspension system as developed for their
light tanks. Also from the Mk IIC provisions were included for
the fitting of a bad weather screen to protect the crew from the
elements when required. The number of the Light Dragon of all
Mks supplied to the British Army is unknown, but would have
been low, for in 1936 a decision was made to revert to wheeled
vehicles for artillery towing as they required less maintenance.
In 1939 several gun batteries sent to France as part of the
British Expeditionary Force were using the Light Dragon Mk II.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: Unknown
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R

Light Dragon Mk II
Another line of artillery tractors from Vickers were based on
their series of light tanks. The Light Dragon Mk II was based on
the chassis and suspension of the Light Tank Mk II which had
entered service with the British Army in small numbers during
the early 1930s. Seats were provided for a gun crew of six to
the rear, with ammunition being stored in the central area of
the vehicle. After trials the vehicle was accepted for service with
the British army who would use it for towing weapons such as
the 18 pounder field gun and 4.5 inch howitzer. The Light
Dragon Mk II began to enter service in 1931, and was followed
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 3.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 13 ft 2 ins, Width 6 ft 1 in, Height 5 ft 7 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Meadows 58 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 32 mph, Range 160 miles
Armament: None
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 2 + gun crew
by the Mk IIA, Mk IIB, Mk IIC and Mk IID, the Mk IIC introducing a
revised Horstmann suspension system as developed for their
light tanks. Also from the Mk IIC provisions were included for
the fitting of a bad weather screen to protect the crew from the
elements when required. The number of the Light Dragon of all
Mks supplied to the British Army is unknown, but would have
been low, for in 1936 a decision was made to revert to wheeled
vehicles for artillery towing as they required less maintenance.
In 1939 several gun batteries sent to France as part of the
British Expeditionary Force were using the Light Dragon Mk II.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: Unknown
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R



A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R

A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R

A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R

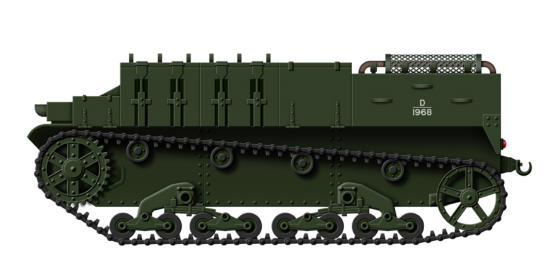
Universal Carrier
In 1934, Vickers-Armstrongs produced a light tracked vehicle as
a private venture that could be used to carry a machine gun or
tow a light field or anti-tank gun. The design was based on the
Carden Loyd tankette that had been developed in the 1920s,
and the British War Office considered it as a replacement for
the light Dragon artillery tractor and purchased 69. A small
number were produced as the Medium Machine Gun Carrier
being armed with a Vickers machine gun, and the Bren Gun
Carrier armed with that gun. Along with these there were the
Scout Carrier and Cavalry Carrier, but production of just a
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 3.75 tons
Dimensions: Length 12 ft, Width 6 ft 9 ins, Height 2 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Ford 85 hp V8 petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 30 mph, Range 150 miles
Armament: 1 x Bren light machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 3
single model was more economical and the Universal carrier
appeared in 1940. By 1945 production in the U.K. amounted to
about 57,000 of all models, while further examples were built
in Canada (29,000), Australia (5,000), New Zealand (1,300) and
the United States (20,000) for their own armed forces. In
service with the British Army, the Universal carrier was used by
reconnaissance regiments, support companies and motor
battalions of armoured division. After World War Two, they
remained in service with the British army until 1960, while
numerous countries purchased withdrawn vehicles.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 113.000
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R
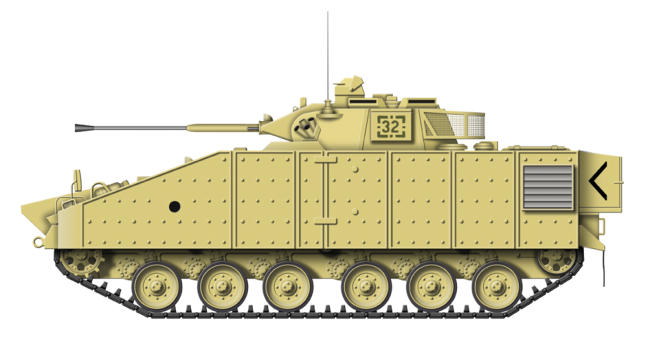
FV432 ‘Trojan’
The development of the FV430 series of vehicles began in the
1950s, the FV432 Trojan being an armoured personnel carrier.
The Trojan had a crew of two and could carry a squad of ten
troops. Te role of the APC is to transport the soldiers over the
battlefield, where on reaching their objective they would
disembark and fight on foot. The troops travel in a rear cabin
which is accessed by a rear door in the hull, seating being side
benches that can be folded up when the vehicle is used as a
cargo carrier. There are also hatches in the roof, but there are
no provisions to allow the use of small arms from inside the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 15.6 tons
Dimensions: Length 17 ft 3 ins, Width 9 ft 2 ins, Height 7 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Rolls-Royce 240 hp multi-fuel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 32 mph, Range 360 miles
Armament: 1 x 30 mm cannon, 1 x 7.62 mm machine gun
Armour: Proof against small arms fire
Crew: 2 + 10 fully equipped troops (or 3.5 tons of cargo)
vehicle. For defence the vehicles were originally equipped with
an unprotected 7.62 mm machine gun, this being superseded
later when the gun was mounted in a small turret. Later a few
Trojans were also fitted with a turret from the Fox armoured
car armed with a 30 mm Rarden cannon to act as fire support
units. The contract for the vehicle was given to GKN Sankey,
who between 1963 and 1971 produced over 3,000 units. High
export sales were hoped for, but in the end the vehicle lost out
to the U.S. M113 which offered a comparable performance at a
much lower price, and failed to find any foreign buyers.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 3,000+
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R


FV432 ‘Trojan’
The development of the FV430 series of vehicles began in the
1950s, the FV432 Trojan being an armoured personnel carrier.
The Trojan had a crew of two and could carry a squad of ten
troops. Te role of the APC is to transport the soldiers over the
battlefield, where on reaching their objective they would
disembark and fight on foot. The troops travel in a rear cabin
which is accessed by a rear door in the hull, seating being side
benches that can be folded up when the vehicle is used as a
cargo carrier. There are also hatches in the roof, but there are
no provisions to allow the use of small arms from inside the
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 15.6 tons
Dimensions: Length 17 ft 3 ins, Width 9 ft 2 ins, Height 7 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Rolls-Royce 240 hp multi-fuel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 32 mph, Range 360 miles
Armament: 1 x 7.62 mm machine gun
Armour: Proof against small arms fire
Crew: 2 + 10 fully equipped troops (or 3.5 tons of cargo)
vehicle. For defence the vehicles were originally equipped with
an unprotected 7.62 mm machine gun, this being superseded
later when the gun was mounted in a small turret. Later a few
Trojans were also fitted with a turret from the Fox armoured
car armed with a 30 mm Rarden cannon to act as fire support
units. The contract for the vehicle was given to GKN Sankey,
who between 1963 and 1971 produced over 3,000 units. High
export sales were hoped for, but in the end the vehicle lost out
to the U.S. M113 which offered a comparable performance at a
much lower price, and failed to find any foreign buyers.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 3,000+
A R M O U R E D P E R S O N N E L C A R R I E R




Universal Carrier
In 1934, Vickers-Armstrongs produced a light tracked vehicle as
a private venture that could be used to carry a machine gun or
tow a light field or anti-tank gun. The design was based on the
Carden Loyd tankette that had been developed in the 1920s,
and the British War Office considered it as a replacement for
the light Dragon artillery tractor and purchased 69. A small
number were produced as the Medium Machine Gun Carrier
being armed with a Vickers machine gun, and the Bren Gun
Carrier armed with that gun. Along with these there were the
Scout Carrier and Cavalry Carrier, but production of just a
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 3.75 tons
Dimensions: Length 12 ft, Width 6 ft 9 ins, Height 2 ft 5 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Ford 85 hp V8 petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 30 mph, Range 150 miles
Armament: 1 x Bren light machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 10 mm
Crew: 3
single model was more economical and the Universal carrier
appeared in 1940. By 1945 production in the U.K. amounted to
about 57,000 of all models, while further examples were built
in Canada (29,000), Australia (5,000), New Zealand (1,300) and
the United States (20,000) for their own armed forces. In
service with the British Army, the Universal carrier was used by
reconnaissance regiments, support companies and motor
battalions of armoured division. After World War Two, they
remained in service with the British army until 1960, while
numerous countries purchased withdrawn vehicles.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 113.000
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R





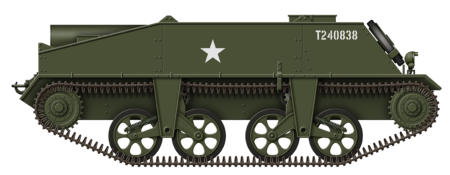


Voroshilovets Prime Mover
Work on a new heavy prime mover for the Soviet army began
in 1935. The vehicle was fully tracked, and was developed as a
more powerful alternative to the Komintern prime mover. The
Voroshilovets used the suspension and running gear of the
T24 tank that had entered service in small numbers during
1931, and were initially powered by a 400 hp diesel engine, this
later being changed to a 375 hp V2V diesel engine, a detuned
version of the engine used in the T34 tank. The Voroshilovets
was the largest of the Russian tracked artillery tractors with a
towing capacity of 22 tons, and was used as the prime mover
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Weight: 15.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 20 ft 5 ins, Width 7 ft 8 ins, Height 9 ft
Powerplant: 1 x 375 hp diesel engine
Performance: Maximum speed 22 mph, Range 167 miles
Armour: None
Crew: 2 + 16 man gun crew
Payload: 3 tons • Towing Capacity: 22 tons
for heavy artillery such as the B4 203 mm tracked howitzer and
the Br5 280 mm heavy mortar. They had a crew of two and
seating for a 16 man gun crew or 3 tons of cargo in the rear
flatbed area which could be fitted with a storm cover in bad
weather. They began to enter service in 1939, and by the time
of the German invasion in 1941 about 230 had been built. In
late 1941 the factory at Kharkov was evacuated and production
transferred to the Stalingrad Tractor Factory. More than 1,100
had been built when production came to end in the autumn of
1942 after the factory was overrun by the Germans.
Country of Origin: USSR
Number Built: 1,100+
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R




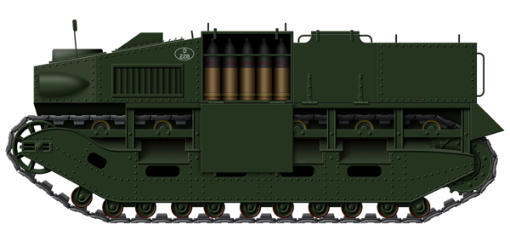
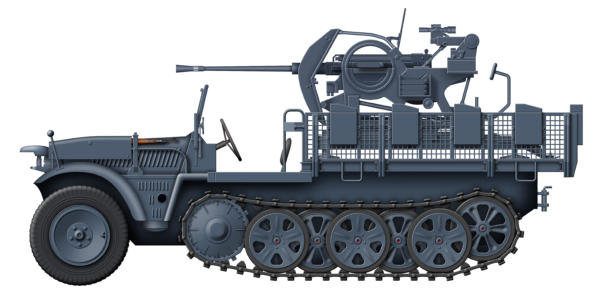
Demag SdKfz 10/5
Design work on the Demag SdKfz 10 series of half-tracks began
in 1934, initially under the guise of a commercial product to
circumvent the terms of the Versaille Treaty. Drive was only
provided to the tracks, the front wheels being non-powered
meant that steering could become difficult in soft terrain. The
suspension was of the torsion bar type and gave the vehicle a
ground clearance of 13 inches (33 cm), which aided the
vehicles good off-road performance, even over uneven terrain.
They had a maximum speed of 47 mph per hour and an
operational range of 190 miles over good surfaces. They were
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Weight: 3.37 tons
Dimensions: Length 15 ft 6 ins, Width 6 ft 3 ins, Height 6 ft 6 ins
Powerplant: 1 x Maybach 99 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 40 mph, Range 190 miles
Armament: 1 x 2 cm FlaK 38 anti-aircraft gun
Armour: None
Crew: 2 + 6 passengers
classified as a lightweight half-track and were given an official
towing capacity of 1 ton, and were intended as an artillery
tractor for light calibre artillery weapons like the 2 cm FlaK 30
anti-aircraft gun up to the lightweight 7.5 cm leIG infantry
support gun. Full scale production began in 1938, with the
SdKfz 10 being seen in many guises during its career. The SfKfz
10/4 mounted the 2 cm FlaK 30 anti-aircraft gun system on a
flatbed, while the SdKfz 10/5 had the faster-firing 2 cm FlaK 38
gun instead. Both of these models featured fold-down panels
that acted as a platform for the gun crew when in action.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Produced: 14,000+
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R



Raupenschlepper OST (RSO/2)
After the Germans invaded the Soviet Union in 1941, they
began to experience the full effects of a Russian autumn and
winter. The primitive roads soon became quagmires, and to
maintain the mobility of the army Steyr proposed a small, fully
tracked vehicle based on its 1500A light truck. They were initial
designed as a prime mover and artillery supply vehicle, and
had a pressed steel cab and a wooden drop-side cargo flatbed.
A simple suspension system was used instead of the complex
interleaved wheel arrangement of most German halftracks
which proved better at handling the conditions of the Russian
S P E C I F I C A T I O N : (RS0/01)
Weight: 3 tons
Dimensions: Length 14 ft 6 ins,
Width 6 ft 4 ins, Height 8 ft 4 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 85 hp Steyr petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 18 mph, Range 186 miles
Armament/Armour: None
Crew: 2
winter, where mud or snow could build up between the wheel
arrangement of a halftrack and freeze which would disable the
vehicle. Named the Raupenschlepper Ost they entered service
in 1942, and although designed as a prime mover they were
soon used for general duties and a wide variety of other roles,
including an ambulance and communication vehicles. To meet
demand new versions appeared. The RSO/2 introduced a new
flat sided cab that was cheaper and easier to produce, while
the RSO itself became one of the workhorses on the eastern
front, and in total over 28,000 were built.
Country of Origin: Germany
Number Built: 28,000+
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R


Crusader Gun Tractor
Another use for withdrawn Crusader tanks was found in the
form of a gun tractor to tow the heavy QF 17 pounder anti-tank
gun which had recently entered service. Ruston & Hornsby
were given the task of conversions who fitted a large armoured
opened topped box superstructure onto the chassis where the
gun crew of six were seated behind the driver when travelling,
and the space at the rear being used to carry ammunition. The
new vehicle was simply called the Crusader Gun Tractor, and
became the main tracked artillery tractor in the British army.
The vehicle was still capable of high speed but was officially
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 18.7 tons
Dimensions: Length 17 ft 2 ins, Width 8 ft 1 in, Height 8 ft 4 ins
Powerplant: 1 x 350 hp Liberty petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 27 mph, Range 100 miles
Armament: None
Armour: 14 mm
Crew: 1 + gun crew
limited to 27 mph, which still could be hard on the towed guns,
especially over rough ground. The crusader Gun Tractor was
used by the British Army in North West Europe from D-Day in
June 1944 until the end of the war, several amso being used as
a reconnaissance or command vehicles for artillery regiments.
The Crusader proved to be a popular vehicle with those that
used it, and many drivers tended to remove the 'governors'
which limited the speed, so they could have an extra burst of
speed in case of an emergency. It was claimed when this was
done an empty Crusader could travel up to 55 mph.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Produced: 400+
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R



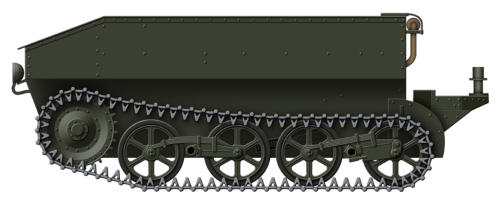
Carden-Loyd Tankette
In the mid 1920s Carden-Loyd began to produce a small one
man tankette based on preliminary work carried out by Major
Giffard LeQuesne Martel. Carden-Loyd then proposed a two-
man version which would prove to be a more effective and
popular idea. The design was accepted for service by the
British Army who placed a small order for the vehicle in 1927.
Shortly after this the firm was acquired by Vickers-Armstrong
who saw a gap in the market for the tankette and the potential
for development. The tankette went through a number of
marks, and by the time production ended in 1935, about 450
S P E C I F I C A T I O N :
Vehicle Weight: 1.5 tons
Dimensions: Length 8 ft 1 ins, Width 5 ft 7 ins, Height 4 ft
Powerplant: 1 x Ford 40 hp petrol engine
Performance: Maximum speed 25 mph, Range 90 miles
Armament: 1 x 0.303 inch or 0.5 inch Vickers machine gun
Armour: Maximum thickness 9 mm
Crew: 2
had been built. The most numerous was the mks VI with at
least 325 being produced, and were used in the British Army as
a machine gun carrier, and to a lesser extent as a mortar
carrier, smoke projector and a light gun tractor for a 37 mm
howitzer or 20 mm anti tank gun. In 1929, Poland and the
Soviet Union both purchased a small number of tankettes with
a licence, who used them to develop the TK and TKS tankette
series (Poland), and the T27 tankette (Soviet Union). Italy, Japan
and Czechoslovakia also purchased a small number or built
licenced copies before developing their own vehicles.
Country of Origin: UK
Number Built: 450
A R T I L L E R Y T R A C T O R

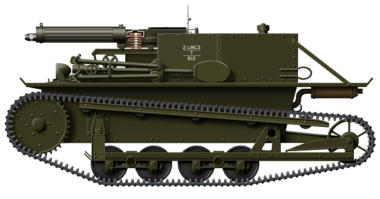








Pages